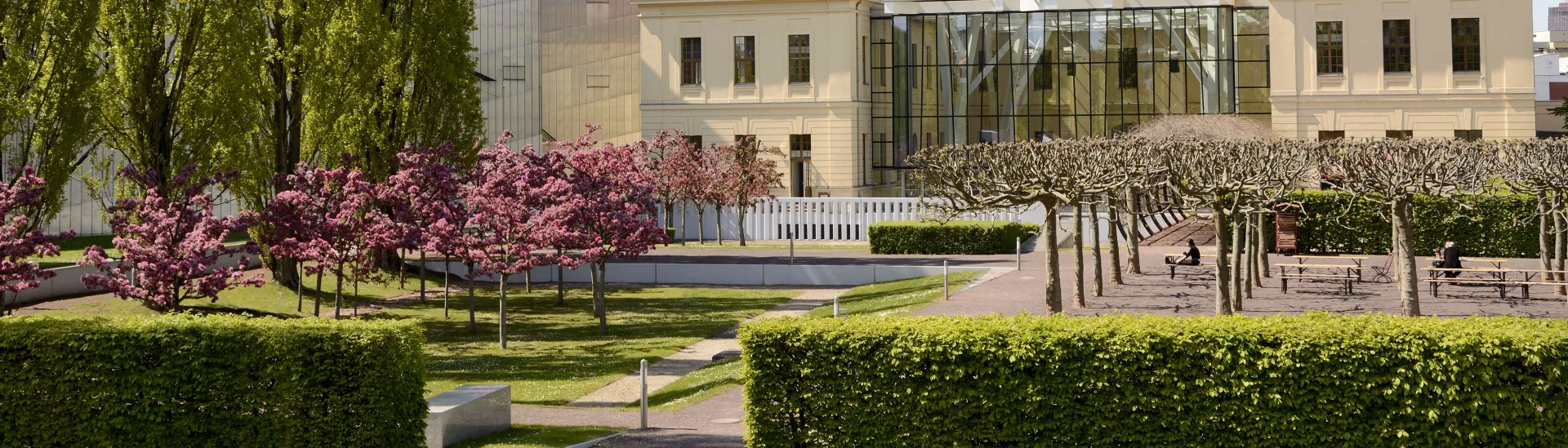

Our Museum Gardens
Green Oases in the Middle of the Kreuzberg District
Two gardens round out the building ensemble of the Libeskind building and the Old Building. They offer our visitors a place to relax and at the same serve as a backdrop for various events such as garden parties for the whole family, concerts, and readings during our annual Cultural Summer Program. Admission to the garden area is of course free of charge.
Where
Museum Garden
Lindenstraße 9–14, 10969 Berlin
The Museum Garden by Kollhoff and Ovaska
A garden was created behind the Old Building between 1984 and 1988 for what was then the Berlin Museum, based on the design by architects Hans Kollhoff and Arthur Ovaska. The project was part of the International Building Exhibition (IBA) and was entered as a garden monument in the list of the Berlin State Office for Historic Monuments. The starkly geometrical garden design includes an arcade, a small cluster of plane trees, and a circular fountain of red granite in the back section. In the summer months our guests can take a break on lounge chairs on the lawns planted with crab apple trees. The garden is also the site of the Sunday concerts in our popular Jazz in the Garden series, part of our Cultural Summer Program.
The Museum Garden by Kollhoff and Ovaska; Jewish Museum Berlin, photo: Jens Ziehe
Views of the Museum Garden
The Gardens around the Libeskind Building
Another garden on the grounds around the Libeskind building, created by Berlin landscape architects Cornelia Müller, Elmar Knippschild, and Jan Wehberg, responds to the architecture’s use of form. Thus the freestanding structures originally planned by Daniel Libeskind in the form of the “voids,” the empty spaces in the interior of the building, are echoed as gravel footprints. A rose garden around the Garden of Exile recalls that in Jerusalem during the days of the Holy Temple, the rose was one of the few plants permitted to be cultivated there on ritual grounds.
Adjacent to the roses, a natural stone relief set into the ground is based on a drawing by artist Gisèle Celan-Lestrange, widow of poet Paul Celan. It continues in the area between the Old Building and the Libeskind building in the Paul Celan courtyard, designed to recall a typical Berlin courtyard.
Views of the Garden around the Libeskind Building
The park extends to the south into the adjacent residential area, thus connecting the Libeskind building with its surroundings. At the end of Alte Jakobstrasse is the Paradise Garden, where a Robinia (false acacia) grove grew as a volunteer atop a postwar pile of rubble. A stone fountain in the shape of a snake and a channel that feeds the fountain at the base of a tree refer to the motif of paradise.
Our Buildings: Daniel Libeskind and the Baroque Era (6)







